Indications
-
ELIQUIS (apixaban) is a prescription
medicine used in adults to reduce the risk of stroke and blood clots in people who have atrial fibrillation (AFib), a type of irregular heartbeat, not caused by a heart valve problem. -
ELIQUIS (apixaban) is a prescription
medicine used in adults to treat blood clots in the veins of your legs (deep vein thrombosis-DVT) or lungs (pulmonary embolism-PE), and to reduce the risk of them occurring again after receiving treatment for blood clots. -
ELIQUIS (apixaban) is a prescription
medicine used in children from birth and older to treat blood clots in the veins of legs and lungs (venous thromboembolism) after at least 5 days of initial anticoagulant treatment, and to reduce the risk of them happening again. ELIQUIS was not studied and is not recommended in children weighing less than 5.7 pounds (2.6 kg). -
ELIQUIS (apixaban) is a prescription
medicine used in adults to help prevent a blood clot in the veins of your legs (deep vein thrombosis-DVT) and lungs (pulmonary embolism-PE) of people who have just had hip or knee replacement surgery.
Indications
-
ELIQUIS (apixaban) is a
prescription medicine used in adults to reduce the risk of stroke and blood clots in people who have atrial fibrillation (AFib), a type of irregular heartbeat, not caused by a heart valve problem. -
ELIQUIS (apixaban) is a
prescription medicine used in adults to treat blood clots in the veins of your legs (deep vein thrombosis-DVT) or lungs (pulmonary embolism-PE), and to reduce the risk of them occurring again after receiving treatment for blood clots. -
ELIQUIS (apixaban) is a
prescription medicine used in children from birth and older to treat blood clots in the veins of legs and lungs (venous thromboembolism) after at least 5 days of initial anticoagulant treatment, and to reduce the risk of them happening again. ELIQUIS was not studied and is not recommended in children weighing less than 5.7 pounds (2.6 kg). -
ELIQUIS (apixaban) is a
prescription medicine used in adults to help prevent a blood clot in the veins of your legs (deep vein thrombosis-DVT) and lungs (pulmonary embolism-PE) of people who have just had hip or knee replacement surgery.
In the 3 sections below, learn how AFib not caused by a heart valve problem can lead to a stroke, understand the role of blood thinners, and get information about ELIQUIS.

I learned that having AFib increases my risk of stroke about 5 times. That made me understand the importance of taking ELIQUIS to help reduce that risk.
Sandy is a paid patient ambassador.

I finally realized it was time to go to the doctor when my heart was skipping beats more constantly, even in bed at night.
Bitsy is a paid patient ambassador.

When I learned more about AFib not caused by a heart valve problem, I was worried when my doctor told me I have a higher risk of stroke.
Tamii is a paid patient ambassador.
DID YOU KNOW?
Patients with AFib not caused by a heart valve problem are ≈5x more likely to have a stroke

The most common type of atrial fibrillation (AFib) is not caused by a heart valve problem. It is also known as nonvalvular AFib, or NVAF.
It is projected that by 2030, approximately 12 million people in the U.S. will have AFib not caused by a heart valve problem. The exact cause of AFib is not always known, but the risk increases as you get older.
What is happening in my heart?

Try to picture your heart as a soft squeeze bottle filled with liquid.
Now imagine pressing very quickly but lightly. You never get all the liquid out the way you would with a full squeeze.
Similarly, in the heart, this can allow blood to pool in the atria, the top chambers of the heart.
Some common symptoms of AFib not caused by a heart valve problem

Heart palpitations

Shortness of breath

Dizziness or fatigue

Chest pain

The symptoms can be different for everyone. Some patients don’t feel any symptoms at all.
How can AFib lead to a stroke in the brain?

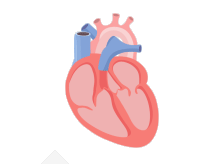
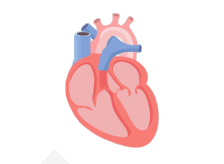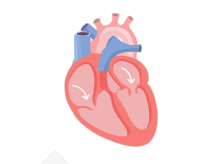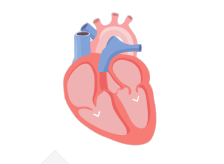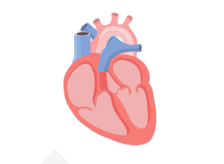
In a healthy heart, the upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the lower chambers (ventricles) and then to the rest of the body


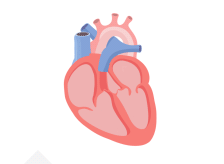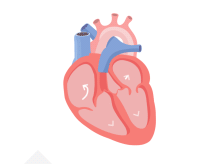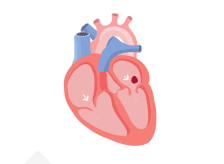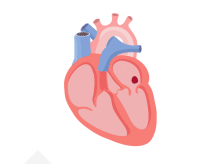
With AFib, the atria quiver instead of pumping with a steady beat. This may cause blood to pool in the atria, which can lead to blood clots forming

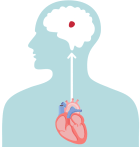
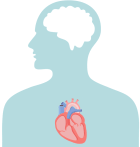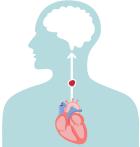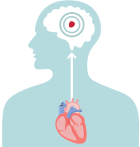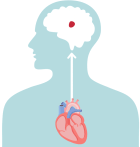
If a blood clot, or piece of it, breaks off, it can travel out of the heart, through the blood vessels, and to the brain—where it can cause a stroke

Since patients with AFib not caused by a heart valve problem are at a higher risk of stroke, it’s important to ask your doctor about treatment options that can help reduce the risk of stroke.

Facts About Stroke
- Strokes related to AFib are often more severe than strokes from other causes
- Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death in the U.S.
- Stroke is a leading cause of disability among Americans
YOU MAY ASK
What is the role of a blood thinner for AFib not caused by a heart valve problem?
Blood thinners are commonly prescribed to reduce the risk of stroke for patients with AFib not caused by a heart valve problem
BLOOD THINNERS WORK TO
 Help reduce the risk of blood clots forming in the atria (upper chambers of the heart)
Help reduce the risk of blood clots forming in the atria (upper chambers of the heart)
 And therefore reduce the risk of stroke due to blood clots in the heart traveling to the brain
And therefore reduce the risk of stroke due to blood clots in the heart traveling to the brain
Choosing a blood thinner with your doctor
For more than 60 years, patients were prescribed a blood thinner called warfarin. These days, you have more choices. Working with your doctor is the first step in learning more about AFib not caused by a heart valve problem, and if ELIQUIS may be a treatment option to reduce the increased risk of stroke.



Please see U.S. Full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNINGS and Medication Guide.

Because they help reduce the risk of blood clots forming, blood thinners increase the risk of bleeding,
which can be serious, and may lead to death.
While taking a blood thinner, you may bruise more easily and it may take longer than usual for any bleeding to stop. Be sure to seek medical attention right away if you have signs or symptoms of bleeding, such as unexpected bleeding or bruising, or bleeding that lasts a long time. You may have a higher risk of bleeding if you take ELIQUIS and take other medicines that increase your risk of bleeding.
Click here for more comprehensive information you should be aware of about bleeding and ELIQUIS. Be sure to call your healthcare provider right away if you fall or injure yourself, especially if you hit your head. Your healthcare provider may need to check you.
Your doctor may encourage you to limit activities that may cause injury and take some precautions, such as:

Take extra care using knives, scissors, and nail clippers

Use an electric razor

Wear shoes or non-skid slippers in the house

Use a soft toothbrush and waxed dental floss

Wear gloves when using sharp tools or doing yard work



WHAT IS ELIQUIS?
ELIQUIS is a prescription medicine used in adults to reduce the risk of stroke and blood clots in patients who have atrial fibrillation (AFib), a type of irregular heartbeat, not caused by a heart valve problem. Only you and your healthcare provider can decide if ELIQUIS is right for you.





In a clinical study
of ADULT patients with
AFib not caused
by
a heart valve
problem


ELIQUIS
REDUCES STROKE RISKin a clinical study vs. warfarin



ELIQUIS HAS
LESS MAJOR BLEEDING
THAN WARFARIN
in a clinical study vs. warfarin



In the same clinical study
over 97% of patients taking ELIQUIS did not experience a strokeOver a 3-year study, a first stroke occurred in 2.9%
of warfarin patients vs. 2.3% of ELIQUIS patients.
In a clinical study of adult patients with AFib not caused by a heart valve problem,
ELIQUIS was proven better than warfarin:
risk
major bleeding*


ELIQUIS and other blood thinners increase the risk of bleeding, which can be serious, and may lead to death. In another study compared to aspirin, ELIQUIS had a modest increase in major bleeding.*
If you’re taking warfarin, consider talking to your doctor about ELIQUIS for both these reasons: ELIQUIS was proven effective to reduce the risk of stroke due to atrial fibrillation (AFib) not caused by a heart valve problem. Plus, ELIQUIS had significantly less major bleeding* than warfarin.
*Major bleeding included noticeable bleeding with at least 1 of the following—a transfusion of 2 or more units of blood; bleeding that occurred in the brain, spine, eye, inside the abdomen, around the heart, in a joint, or in a muscle, leading to damage; or fatal bleeding.
Please see Important Safety Information, including Boxed WARNINGS, below.